Editor: View Mate All Glass Railing
Glass Types for Railings
1.Float Glass (Pilkington Process)
Manufacturing: Molten glass floated on molten tin to achieve uniform thickness.
Characteristics:
Non-tempered, basic structural properties.
Rarely used in railings without further processing.
2.Annealed Glass
Process: Slow cooling in a lehr kiln to relieve internal stresses.
Limitations:
Prone to thermal/mechanical shock.
Break Pattern: Dangerous large shards (non-compliant with safety standards)
3.Heat-Strengthened Glass
Process: Heated to 650°C, cooled moderately (2× strength of annealed).
Applications: Curtain walls where full tempering isn’t required.
Break Pattern: Larger fragments than tempered (partial safety)
4.Tempered Glass
Process: Rapid quenching at 700°C (4-5× stronger than annealed).
Safety Compliance:
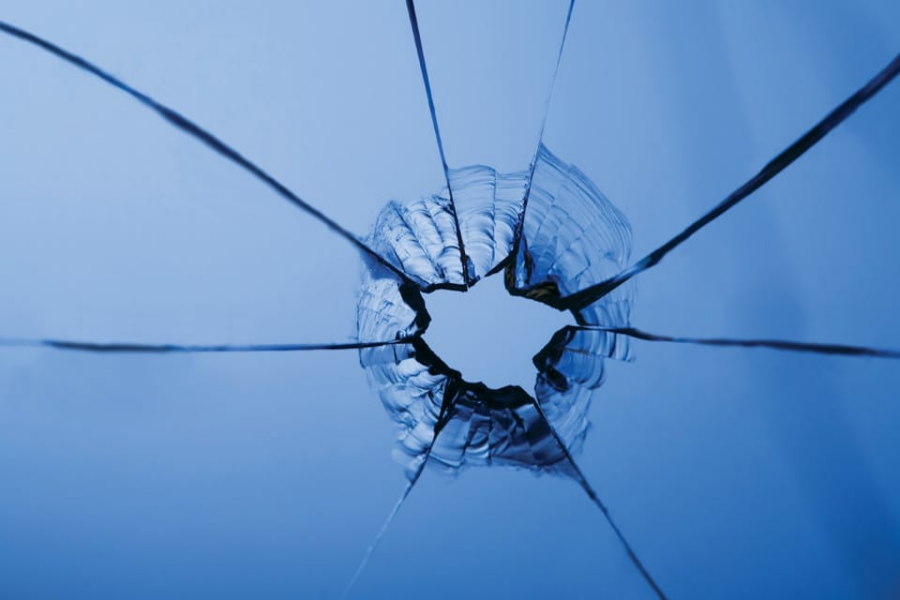
Break Pattern: Granular fragments (EN 12150/CPSC 1201 certified). Mandatory for freestanding balustrades.
Risk: Spontaneous breakage due to impurities.
Solution: Heat soaking at 290°C for 2 hours to eliminate unstable NiS.
5.Glazing Systems Comparison
|
System |
Advantages | Limitations |
|
Wet Glaze |
- Superior weather resistance |
- Portland cement damages PVB |
|
(Gypsum/Silicone) |
- Ideal for curved installations |
- 24-48hr curing time |
|
Dry Glaze |
- 80% faster installation |
- Higher material cost |
| (Gasket/Clamp) | - No curing required |
- Limited to straight runs |
6.Structural Loads
Linear Load: 50 plf (0.73 kN/m)
Concentrated Load: 200 lbs (0.89 kN) at top edge.
Laminated Glass Mandate
Post-2015 IBC: All railings require laminated glass (≥2 plies, equal thickness).
Exception: Monolithic tempered glass permitted only if no walking surface below
7.Top Rail Exemption
Allowed if:
Laminated glass passes load tests (ASCE 7).
Approved by local building official (2018 IBC removes this requirement).
Edge Finishes & Durability
Key Concern: Ionoplast interlayers outperform PVB in humidity resistance.
8.Common Failure Modes
Nelophobia Triggers:
Nickel sulfide inclusions (heat soaking reduces risk by 95%).
Improper edge alignment (ASTM C1172 compliance critical).
9.Wind-Borne Debris Zones
Wind-borne debris regions include the Gulf of Mexico, Atlantic coastline, Hawaii • Balusters and in-fill panels shall be laminated glass • Glass supporting top rail – The assembly shall be tested according to the impact requirements – Top rail shall remain in place after impact
10.Conclusions
Railing systems designed with laminated glass provide safety and glass retention after breakage • Ionoplast interlayers are stronger, deflect less, and provide better post-glass breakage performance in minimally supported railings • Building code requirements for railings allow laminated glass and, in some cases, require laminated glass for missile impact and structural glass systems • Sealant compatibility and glazing support details require special attention
Post time: Jun-25-2025